Download Fortinet FCSS - Enterprise Firewall 7.6 Administrator.FCSS_EFW_AD-7.6.Braindump2go.2025-10-28.25q.vcex
| Vendor: | Fortinet |
| Exam Code: | FCSS_EFW_AD-7.6 |
| Exam Name: | Fortinet FCSS - Enterprise Firewall 7.6 Administrator |
| Date: | Oct 28, 2025 |
| File Size: | 1 MB |
| Downloads: | 7 |
How to open VCEX files?
Files with VCEX extension can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Discount: 20%
Demo Questions
Question 1
A company that acquired multiple branches across different countries needs to install new FortiGate devices on each of those branches. However, the IT staff lacks sufficient knowledge to implement the initial configuration on the FortiGate devices.
Which three approaches can the company take to successfully deploy advanced initial configurations on remote branches? (Choose three.)
- Use metadata variables to dynamically assign values according to each FortiGate device.
- Use provisioning templates and install configuration settings at the device layer.
- Use the Global ADOM to deploy global object configurations to each FortiGate device.
- Apply Jinja in the FortiManager scripts for large-scale and advanced deployments.
- Add FortiGate devices on FortiManager as model devices, and use ZTP or LTP to connect to FortiGate devices.
Correct answer: ABE
Explanation:
Use metadata variables to dynamically assign values according to each FortiGate device:Metadata variables in FortiManager allow device-specific configurations to be dynamically assigned without manually configuring each FortiGate. This is especially useful when deploying multiple devices with similar base configurations.Use provisioning templates and install configuration settings at the device layer:Provisioning templates in FortiManager provide a structured way to configure FortiGate devices. These templates can define interfaces, policies, and settings, ensuring that each device is correctly configured upon deployment.Add FortiGate devices on FortiManager as model devices, and use ZTP or LTP to connect to FortiGate devices:Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP) and Local Touch Provisioning (LTP) help automate the deployment of FortiGate devices. By adding devices as model devices in FortiManager, configurations can be pushed automatically when devices connect for the first time, reducing manual effort. Use metadata variables to dynamically assign values according to each FortiGate device:
Metadata variables in FortiManager allow device-specific configurations to be dynamically assigned without manually configuring each FortiGate. This is especially useful when deploying multiple devices with similar base configurations.
Use provisioning templates and install configuration settings at the device layer:
Provisioning templates in FortiManager provide a structured way to configure FortiGate devices. These templates can define interfaces, policies, and settings, ensuring that each device is correctly configured upon deployment.
Add FortiGate devices on FortiManager as model devices, and use ZTP or LTP to connect to FortiGate devices:
Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP) and Local Touch Provisioning (LTP) help automate the deployment of FortiGate devices. By adding devices as model devices in FortiManager, configurations can be pushed automatically when devices connect for the first time, reducing manual effort.
Question 2
An administrator is checking an enterprise network and sees a suspicious packet with the MAC address e0:23:ff:fc:00:86.
What two conclusions can the administrator draw? (Choose two.)
- The suspicious packet is related to a cluster that has VDOMs enabled.
- The network includes FortiGate devices configured with the FGSP protocol.
- The suspicious packet is related to a cluster with a group-id value lower than 255.
- The suspicious packet corresponds to port 7 on a FortiGate device.
Correct answer: AC
Explanation:
The MAC address e0:23:ff:fc:00:86 follows the format used in FortiGate High Availability (HA) clusters. When FortiGate devices are in an HA configuration, they use virtual MAC addresses for failover and redundancy purposes.The suspicious packet is related to a cluster that has VDOMs enabled:FortiGate devices with Virtual Domains (VDOMs) enabled use specific MAC address ranges to differentiate HA-related traffic. This MAC address is likely part of that mechanism.The suspicious packet is related to a cluster with a group-id value lower than 255:FortiGate HA clusters assign virtual MAC addresses based on the group ID. The last octet (00:86) corresponds to a group ID that is below 255, confirming this option. The MAC address e0:23:ff:fc:00:86 follows the format used in FortiGate High Availability (HA) clusters. When FortiGate devices are in an HA configuration, they use virtual MAC addresses for failover and redundancy purposes.
The suspicious packet is related to a cluster that has VDOMs enabled:
FortiGate devices with Virtual Domains (VDOMs) enabled use specific MAC address ranges to differentiate HA-related traffic. This MAC address is likely part of that mechanism.
The suspicious packet is related to a cluster with a group-id value lower than 255:
FortiGate HA clusters assign virtual MAC addresses based on the group ID. The last octet (00:86) corresponds to a group ID that is below 255, confirming this option.
Question 3
A company’s guest internet policy, operating in proxy mode, blocks access to Artificial Intelligence Technology sites using FortiGuard. However, a guest user accessed a page in this category using port 8443.
Which configuration changes are required for FortiGate to analyze HTTPS traffic on nonstandard ports like 8443 when full SSL inspection is active in the guest policy?
- Add a URL wildcard domain to the website CA certificate and use it in the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile.
- In the Protocol Port Mapping section of the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile, enter 443, 8443 to analyze both standard (443) and non-standard (8443) HTTPS ports.
- To analyze nonstandard ports in web filter profiles, use TLSv1.3 in the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile.
- Administrators can block traffic on nonstandard ports by enabling the SNI check in the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile.
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
When FortiGate is operating in proxy mode with full SSL inspection enabled, it inspects encrypted HTTPS traffic by default on port 443. However, some websites may use non-standard HTTPS ports (such as 8443), which FortiGate does not inspect unless explicitly configured.To ensure that FortiGate inspects HTTPS traffic on port 8443, administrators must manually add port 8443 in the Protocol Port Mapping section of the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile. This allows FortiGate to treat HTTPS traffic on port 8443 the same as traffic on port 443, enabling proper inspection and enforcement of FortiGuard category-based web filtering. When FortiGate is operating in proxy mode with full SSL inspection enabled, it inspects encrypted HTTPS traffic by default on port 443. However, some websites may use non-standard HTTPS ports (such as 8443), which FortiGate does not inspect unless explicitly configured.
To ensure that FortiGate inspects HTTPS traffic on port 8443, administrators must manually add port 8443 in the Protocol Port Mapping section of the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile. This allows FortiGate to treat HTTPS traffic on port 8443 the same as traffic on port 443, enabling proper inspection and enforcement of FortiGuard category-based web filtering.
Question 4
An administrator needs to install an IPS profile without triggering false positives that can impact applications and cause problems with the user’s normal traffic flow.
Which action can the administrator take to prevent false positives on IPS analysis?
- Use the IPS profile extension to select an operating system, protocol, and application for all the network internal services and users to prevent false positives.
- Enable Scan Outgoing Connections to avoid clicking suspicious links or attachments that can deliver botnet malware and create false positives.
- Use an IPS profile with action monitor, however, the administrator must be aware that this can compromise network integrity.
- Install missing or expired SSUTLS certificates on the client PC to prevent expected false positives.
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
False positives in Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) analysis can disrupt legitimate traffic and negatively impact user experience. To reduce false positives while maintaining security, administrators can:Use IPS profile extensions to fine-tune the settings based on the organization’s environment.Select the correct operating system, protocol, and application types to ensure that IPS signatures match the network’s actual traffic patterns, reducing false positives.Customize signature selection based on the network’s specific services, filtering out unnecessary or irrelevant signatures. False positives in Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) analysis can disrupt legitimate traffic and negatively impact user experience. To reduce false positives while maintaining security, administrators can:
- Use IPS profile extensions to fine-tune the settings based on the organization’s environment.
- Select the correct operating system, protocol, and application types to ensure that IPS signatures match the network’s actual traffic patterns, reducing false positives.
- Customize signature selection based on the network’s specific services, filtering out unnecessary or irrelevant signatures.
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a hub and spokes deployment.
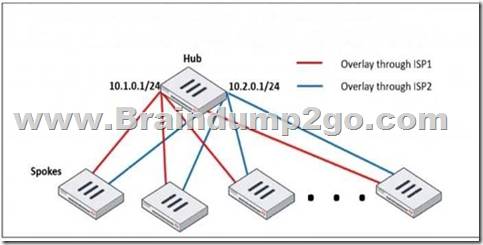
An administrator is deploying several spokes, including the BGP configuration for the spokes to connect to the hub.
Which two commands allow the administrator to minimize the configuration? (Choose two.)
- neighbor-group
- route-reflector-client
- neighbor-range
- ibgp-enforce-multihop
Correct answer: AC
Explanation:
neighbor-group:This command is used to group multiple BGP neighbors with the same configuration, reducing redundant configuration.Instead of defining individual BGP settings for each spoke, the administrator can create a neighbor-group and apply the same policies, reducing manual work.neighbor-range:This command allows the configuration of a range of neighbor IPs dynamically, reducing the need to manually define each spoke neighbor.It automatically adds BGP neighbors that match a given prefix, simplifying deployment. neighbor-group:
- This command is used to group multiple BGP neighbors with the same configuration, reducing redundant configuration.
- Instead of defining individual BGP settings for each spoke, the administrator can create a neighbor-group and apply the same policies, reducing manual work.
neighbor-range:
- This command allows the configuration of a range of neighbor IPs dynamically, reducing the need to manually define each spoke neighbor.
- It automatically adds BGP neighbors that match a given prefix, simplifying deployment.
Question 6
Why does the ISDB block layers 3 and 4 of the OSI model when applying content filtering? (Choose two.)
- FortiGate has a predefined list of all IPs and ports for specific applications downloaded fromFortiGuard.
- The ISDB blocks the IP addresses and ports of an application predefined by FortiGuard.
- The ISDB works in proxy mode, allowing the analysis of packets in layers 3 and 4 of the OSI model.
- The ISDB limits access by URL and domain.
Correct answer: AB
Explanation:
The Internet Service Database (ISDB) in FortiGate is used to enforce content filtering at Layer 3 (Network Layer) and Layer 4 (Transport Layer) of the OSI model by identifying applications based on their predefined IP addresses and ports.FortiGate has a predefined list of all IPs and ports for specific applications downloaded from FortiGuard:FortiGate retrieves and updates a predefined list of IPs and ports for different internet services from FortiGuard.This allows FortiGate to block specific services at Layer 3 and Layer 4 without requiring deep packet inspection.The ISDB blocks the IP addresses and ports of an application predefined by FortiGuard:ISDB works by matching traffic to known IP addresses and ports of categorized services.When an application or service is blocked, FortiGate prevents communication by denying traffic based on its destination IP and port number. The Internet Service Database (ISDB) in FortiGate is used to enforce content filtering at Layer 3 (Network Layer) and Layer 4 (Transport Layer) of the OSI model by identifying applications based on their predefined IP addresses and ports.
FortiGate has a predefined list of all IPs and ports for specific applications downloaded from FortiGuard:
- FortiGate retrieves and updates a predefined list of IPs and ports for different internet services from FortiGuard.
- This allows FortiGate to block specific services at Layer 3 and Layer 4 without requiring deep packet inspection.
The ISDB blocks the IP addresses and ports of an application predefined by FortiGuard:
- ISDB works by matching traffic to known IP addresses and ports of categorized services.
- When an application or service is blocked, FortiGate prevents communication by denying traffic based on its destination IP and port number.
Question 7
Refer to the exhibits.
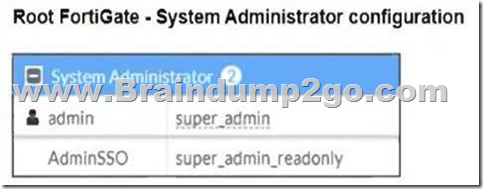
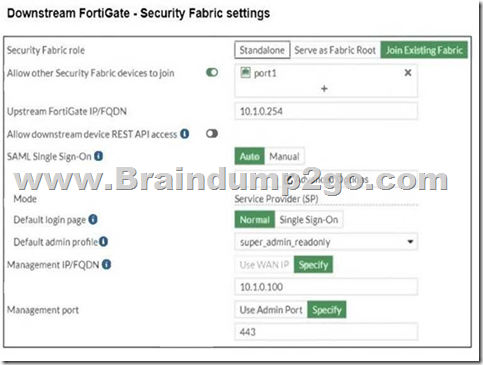
The Administrators section of a root FortiGate device and the Security Fabric Settings section of a downstream FortiGate device are shown.
When prompted to sign in with Security Fabric in the downstream FortiGate device, a user enters the AdminSSO credentials.
What is the next status for the user?
- The user is prompted to create an SSO administrator account for AdminSSO.
- The user receives an authentication failure message.
- The user accesses the downstream FortiGate with super_admin_readonly privileges.
- The user accesses the downstream FortiGate with super_admin privileges.
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
From the Root FortiGate – System Administrator Configuration exhibit:The AdminSSO account has the super_admin_readonly role.From the Downstream FortiGate – Security Fabric Settings exhibit:The Security Fabric role is set to Join Existing Fabric, meaning it will authenticate with the root FortiGate.SAML Single Sign-On (SSO) is enabled, and the default admin profile is set to super_admin_readonly.When the AdminSSO user logs into the downstream FortiGate using SSO, the authentication request is sent to the root FortiGate, where AdminSSO has super_admin_readonly permissions. Since the downstream FortiGate inherits this permission through the Security Fabric configuration, the user will be granted super_admin_readonly access. From the Root FortiGate – System Administrator Configuration exhibit:
- The AdminSSO account has the super_admin_readonly role.
From the Downstream FortiGate – Security Fabric Settings exhibit:
- The Security Fabric role is set to Join Existing Fabric, meaning it will authenticate with the root FortiGate.
- SAML Single Sign-On (SSO) is enabled, and the default admin profile is set to super_admin_readonly.
When the AdminSSO user logs into the downstream FortiGate using SSO, the authentication request is sent to the root FortiGate, where AdminSSO has super_admin_readonly permissions. Since the downstream FortiGate inherits this permission through the Security Fabric configuration, the user will be granted super_admin_readonly access.
Question 8
A user reports that their computer was infected with malware after accessing a secured HTTPS website. However, when the administrator checks the FortiGate logs, they do not see that the website was detected as insecure despite having an SSL certificate and correct profiles applied on the policy.
How can an administrator ensure that FortiGate can analyze encrypted HTTPS traffic on a website?
- The administrator must enable reputable websites to allow only SSL/TLS websites rated by FortiGuard web filter.
- The administrator must enable URL extraction from SNI on the SSL certificate inspection to ensure the TLS three-way handshake is correctly analyzed by FortiGate.
- The administrator must enable DNS over TLS to protect against fake Server Name Indication (SNI) that cannot be analyzed in common DNS requests on HTTPS websites.
- The administrator must enable full SSL inspection in the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile to decrypt packets and ensure they are analyzed as expected.
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
FortiGate, like other security appliances, cannot analyze encrypted HTTPS traffic unless it decrypts it first. If only certificate inspection is enabled, FortiGate can see the certificate details (such as the domain and issuer) but cannot inspect the actual web content.To fully analyze the traffic and detect potential malware threats:Full SSL inspection (Deep Packet Inspection) must be enabled in the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile.This allows FortiGate to decrypt the HTTPS traffic, inspect the content, and then re-encrypt it before forwarding it to the user.Without full SSL inspection, threats embedded in encrypted traffic may go undetected. FortiGate, like other security appliances, cannot analyze encrypted HTTPS traffic unless it decrypts it first. If only certificate inspection is enabled, FortiGate can see the certificate details (such as the domain and issuer) but cannot inspect the actual web content.
To fully analyze the traffic and detect potential malware threats:
- Full SSL inspection (Deep Packet Inspection) must be enabled in the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile.
- This allows FortiGate to decrypt the HTTPS traffic, inspect the content, and then re-encrypt it before forwarding it to the user.
- Without full SSL inspection, threats embedded in encrypted traffic may go undetected.
Question 9
Refer to the exhibit, which shows an ADVPN network.
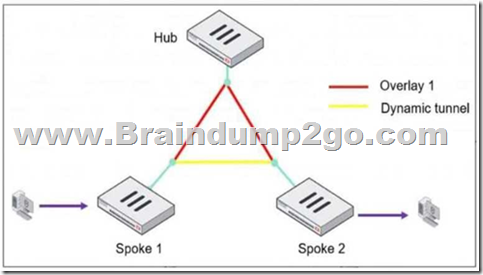
The client behind Spoke-1 generates traffic to the device located behind Spoke-2.
What is the first message that the hub sends to Spoke-1 to bring up the dynamic tunnel?
- Shortcut query
- Shortcut offer
- Shortcut reply
- Shortcut forward
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
In an ADVPN (Auto-Discovery VPN) network, a dynamic VPN tunnel is established on-demand between spokes to optimize traffic flow and reduce latency.Process:1. Traffic Initiation:A client behind Spoke-1 sends traffic to a device behind Spoke-2.The traffic initially flows through the hub, following the pre-established overlay tunnel.2. Hub Detection:The hub detects that Spoke-1 is communicating with Spoke-2 and determines that a direct shortcut tunnel between the spokes can optimize the connection.3. Shortcut Offer:The hub sends a “Shortcut Offer” message to Spoke-1, informing it that a direct dynamic tunnel to Spoke-2 is possible.4. Tunnel Establishment:Spoke-1 and Spoke-2 then negotiate and establish a direct IPsec tunnel for communication. In an ADVPN (Auto-Discovery VPN) network, a dynamic VPN tunnel is established on-demand between spokes to optimize traffic flow and reduce latency.
Process:
1. Traffic Initiation:
A client behind Spoke-1 sends traffic to a device behind Spoke-2.
The traffic initially flows through the hub, following the pre-established overlay tunnel.
2. Hub Detection:
The hub detects that Spoke-1 is communicating with Spoke-2 and determines that a direct shortcut tunnel between the spokes can optimize the connection.
3. Shortcut Offer:
The hub sends a “Shortcut Offer” message to Spoke-1, informing it that a direct dynamic tunnel to Spoke-2 is possible.
4. Tunnel Establishment:
Spoke-1 and Spoke-2 then negotiate and establish a direct IPsec tunnel for communication.
Question 10
What is the initial step performed by FortiGate when handling the first packets of a session?
- Installation of the session key in the network processor (NP)
- Data encryption and decryption
- Security inspections such as ACL, HPE, and IP integrity header checking
- Offloading the packets directly to the content processor (CP)
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
When FortiGate processes the first packets of a session, it follows a sequence of steps to determine how the traffic should be handled before establishing a session. The initial step involves:Access Control List (ACL) checks: Determines if the traffic should be allowed or blocked based on predefined security rules.Hardware Packet Engine (HPE) inspections: Ensures that packet headers are valid and comply with protocol standards.IP Integrity Header Checking: Verifies if the IP headers are intact and not malformed or spoofed. Once these security inspections are completed and the session is validated, FortiGate then installs the session in hardware (if offloading is enabled) or processes it in software. When FortiGate processes the first packets of a session, it follows a sequence of steps to determine how the traffic should be handled before establishing a session. The initial step involves:
- Access Control List (ACL) checks: Determines if the traffic should be allowed or blocked based on predefined security rules.
- Hardware Packet Engine (HPE) inspections: Ensures that packet headers are valid and comply with protocol standards.
- IP Integrity Header Checking: Verifies if the IP headers are intact and not malformed or spoofed. Once these security inspections are completed and the session is validated, FortiGate then installs the session in hardware (if offloading is enabled) or processes it in software.
Question 11
An administrator applied a block-all IPS profile for client and server targets to secure the server, but the database team reported the application stopped working immediately after.
How can an administrator apply IPS in a way that ensures it does not disrupt existing applications in the network?
- Use an IPS profile with all signatures in monitor mode and verify patterns before blocking.
- Limit the IPS profile to server targets only to avoid blocking connections from the server to clients.
- Select flow mode in the IPS profile to accurately analyze application patterns.
- Set the IPS profile signature action to default to discard all possible false positives.
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
Applying an aggressive IPS profile without prior testing can disrupt legitimate applications by incorrectly identifying normal traffic as malicious. To prevent disruptions while still monitoring for threats:Enable IPS in “Monitor Mode” first:This allows FortiGate to log and analyze potential threats without actively blocking traffic.Administrators can review logs and fine-tune IPS signatures to minimize false positives before switching to blocking mode.Verify and adjust signature patterns:Some signatures might trigger unnecessary blocks for legitimate application traffic.By analyzing logs, administrators can disable or modify specific rules causing false positives. Applying an aggressive IPS profile without prior testing can disrupt legitimate applications by incorrectly identifying normal traffic as malicious. To prevent disruptions while still monitoring for threats:
- Enable IPS in “Monitor Mode” first:
- This allows FortiGate to log and analyze potential threats without actively blocking traffic.
- Administrators can review logs and fine-tune IPS signatures to minimize false positives before switching to blocking mode.
- Verify and adjust signature patterns:
- Some signatures might trigger unnecessary blocks for legitimate application traffic.
- By analyzing logs, administrators can disable or modify specific rules causing false positives.
HOW TO OPEN VCE FILES
Use VCE Exam Simulator to open VCE files

HOW TO OPEN VCEX AND EXAM FILES
Use ProfExam Simulator to open VCEX and EXAM files


ProfExam at a 20% markdown
You have the opportunity to purchase ProfExam at a 20% reduced price
Get Now!




